A teenager avoiding tedious tasks writes an AI algorithm that discovers millions of space objects, earns him a quarter of a million, and demonstrates the immense power of even small AI, writes Satyen K. Bordoloi.
18-year-old Matteo Paz is a typical teenager. Hence, when he landed a fancy high school internship at Caltech and received 200 terabytes of infrared data from NASA’s NEOWISE telescope, he reacted as any teen would: he began racking his brain to figure out how not to do it and yet somehow do it. Instead of suffering through manual sorting like most interns would, Paz created an AI algorithm to handle the grunt work.
To his, Caltech’s and NASA’s surprise, his algorithm uncovered 1.5 million space objects nobody knew existed – black holes, supernovae, you name it – all hiding in plain sight within the data noise. Paz, astonished, was awarded $250,000 under the Regeneron Science Talent Search for this. But more than money it is one of the innumerable celebratory tales about AI that usually doesn’t get reported, yet shows that AI can solve our greatest problems, most crucially in data crunching.
If we stop panicking about a robot apocalypse, we will begin to see how it is quietly revolutionising our understanding of the world’s most complex data problems. In doing so, it is changing the world in more ways than we care to acknowledge.
The Cosmic Data Detective: NASA’s NEOWISE telescope was originally designed to find asteroids near Earth. However, its infrared sensors can also detect objects much farther out in space – things hidden behind interstellar dust clouds. These signals were buried within a vast amount of data that would overwhelm most human analysts: a decade’s worth of infrared surveys covering our entire sky.
That’s where Paz’s AI excelled. His algorithm analysed over 450 million objects, learned to identify subtle infrared radiation patterns, and transformed what was essentially an asteroid-hunting dataset into a treasure map of 1.9 million variable objects – of which 1.5 million were entirely new discoveries. We’re talking about black holes emitting energy jets and stars undergoing supernovae – those cosmic drama queens that help us comprehend odd phenomena like dark energy and why the universe continues to expand at an accelerating rate, and perhaps even reveal the ultimate fate of everything, everywhere, one day.
The algorithm didn’t just crunch numbers; it completely overturned the telescope’s purpose. It’s like finding out your old flip phone could actually predict stock markets if you just installed the right app.
If you thought this AI algorithmic analysis by an 18-year-old was a fluke, you’ll be surprised to know that the pattern is repeating itself. Everywhere AI is directed, like a torch, it illuminates old data to provide new insights. At Mount Sinai Hospital, AI is sifting through dusty medical records to discover early warning signs for Alzheimer’s disease years before symptoms appear. Climate scientists are harnessing AI to analyze decades of weather data, enabling predictions of when the next devastating hurricane or heatwave might strike. AI thrives in chaos, uncovering patterns where we thought they did not exist.

Not All AI Wants to Destroy Humanity: Look, I understand that most AI stories can seem terrifying. Algorithmic bias! Deepfakes! Killer robots! However, for every alarming headline, there are countless stories like Paz’s that rarely make the front page, and I try to highlight them whenever I can. His cosmic catalogue is already aiding astronomers in studying binary stars and planets outside our solar system, and he has shared the framework of his algorithm so that other researchers can build upon it.
As I wrote in that article, AI isn’t just lurking in research labs waiting to plot world domination – it is actually out there saving lives right now. DeepMind’s flood prediction system gives people crucial hours to evacuate before rivers burst their banks. One Concern is mapping wildfires and helping firefighters evolve their strategies. In Spain, AutoGrid is managing renewable energy sources so efficiently that some communities are barely using fossil fuels anymore. And don’t get me started on those AI-designed solid-state batteries set to overhaul electric vehicles. Even farmers are getting in on the action, with Blue River’s robots spraying weeds with remarkable precision, while CropX sensors are transforming dusty wasteland into fertile farmland.
Let’s also not forget AI’s applications in cybersecurity, disease prevention, education, and traffic management, as well as in counselling, where AI is creating tools that essentially democratise expertise, bringing high-level knowledge to places and people who have been left behind. It’s like science fiction, except it’s happening right outside your window.
Paz’s NEOWISE AI magic is just the tip of the iceberg. Researchers are uncovering data goldmines that have been hiding in plain sight across nearly every field, discovering ways to extract new value from data that others have overlooked. I’ve covered some before, and now I’ll detail additional ways AI is guiding us toward a bright future.
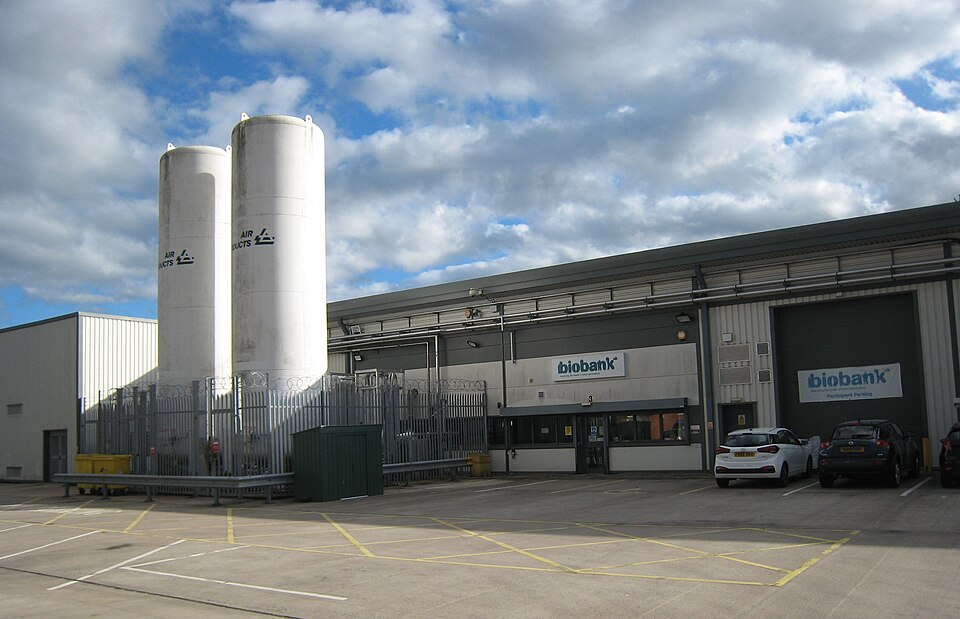
Medical Mysteries: Consider the millions of X-rays, tissue samples, and genetic sequences gathering digital dust in hospital databases and labs worldwide. What secrets are they hiding that will require an AI key to unlock? In 2017, Stanford researchers trained an AI to detect skin cancer by analysing 130,000 historical dermatology images, and it has since become as accurate as actual oncologists with years of training. The UK Biobank project is utilising AI to connect decades-old health records with genetic markers and, in doing so, is uncovering surprising links between lifestyle choices and diseases like Parkinson’s. These dusty digital archives are proving to be living libraries of medical insights under the spotlight of AI.
Climate Crisis Hacks: Climate models are a mishmash of different data types, including ice cores, ocean temperatures, water temperatures, satellite images of disappearing forests and ice, etc. AI can somehow make sense of this jumble, connecting seemingly unconnected dots. Google’s Flood Hub now predicts floods in 80 countries by combining satellite imagery, river measurements, and soil moisture data. At the same time, Carbon Tracker AI monitors methane leaks from oil fields via satellite, making it that much harder for polluters to conceal their environmental crimes.

Classroom Revolution: AI is personalising education by reinterpreting student performance. China’s Squirrel AI analyses millions of homework responses to identify knowledge gaps and customize lessons. In refugee camps, UNESCO’s “Can’t Wait to Learn” program, developed in Holland, adjusts math games according to a child’s progress, effectively overcoming language barriers.
Space: The Final Data Frontier: Paz’s discovery is part of a larger trend in automated space exploration utilising AI. The upcoming Vera C. Rubin Observatory will utilize machine learning to process 60 petabytes (approximately 60 million gigabytes) of galactic data, mapping dark matter and tracking asteroid paths. NASA’s Earth Observing System leverages AI to reinterpret satellite data for agriculture and disaster relief, indicating that the true value of space technology may lie in how we interpret the data rather than simply in its collection. By doing so, we can harvest the data crops, leaving the threshing, cleaning, and processing to AI.
Keeping AI on the Right Path: As AI gets smarter, we need to get wiser about guiding it. Paz’s algorithm worked because it was driven by human curiosity, another reminder that AI can do its best work in partnerships with scientists, ethicists, and communities, and not by replacing them.
Frameworks like the EU’s AI Act and the Montreal Declaration for Responsible AI, which aims to guide the development of AI towards the well-being of all, drive transparency and accountability in tech. In healthcare, new federated learning systems enable hospitals to train AI models on patient data without compromising patient privacy. Conservation platforms like EarthRanger pull together sensor data to protect endangered species while respecting Indigenous land rights.
Paz himself understands this balance. After winning his award, he says he wants to work next on combining AI’s analytical power with humanitarian goals; his first stop – using infrared satellites to monitor wildfire risks. He also wants to use AI to resolve the “Hubble tension” – a puzzling cosmic discrepancy about the rate of universe expansion.
Whether he cracks that problem or not, his curiosity, collaboration, and ethics-driven approach demonstrate what AI can be at its best. By making sense of messy data, challenging doom-and-gloom narratives, and uncovering value in previously ignored information, AI is reshaping fields ranging from cancer research to classroom teaching. In creating systems for discovery rather than profit, works like those done by Paz show that AI can not just illuminate distant galaxies but also the best bits of human nature.
In case you missed:
- Quantum Leaps in Science: AI as the Assembly Line of Discovery
- A Data Centre on the Moon – From Sci-Fi to Necessity
- Rogue AI on the Loose: Can Auditing Uncover Hidden Agendas on Time?
- The End of SEO as We Know It: Welcome to the AIO Revolution
- The Great Data Famine: How AI Ate the Internet (And What’s Next)
- How Old Are We: Shocking New Finding Upends History of Our Species
- Rethinking AI Research: Shifting Focus Towards Human-Level Intelligence
- Are Hallucinations Good For AI? Maybe Not, But They’re Great For Humans
- Copy Of A Copy: Content Generated By AI, Threat To AI Itself
- Forget Smart Homes – Welcome to Your ‘Feeling’ Home









