One-third of food produced for human use is wasted and is a key driver to global hunger, says Felista.
It is unfortunate that 811 million people go hungry every day, despite the fact that one-third of food produced for human use is wasted. Food waste, according to the United Nations World Food Program, is a key driver to global hunger.
Food waste is also considered a humanitarian issue as it not only harms people but also has a harmful impact on our ecosystem. According to World Wide Fund for Nature studies, agricultural emissions account for around 16% of global greenhouse gas emissions, which include gases created when food decomposes.
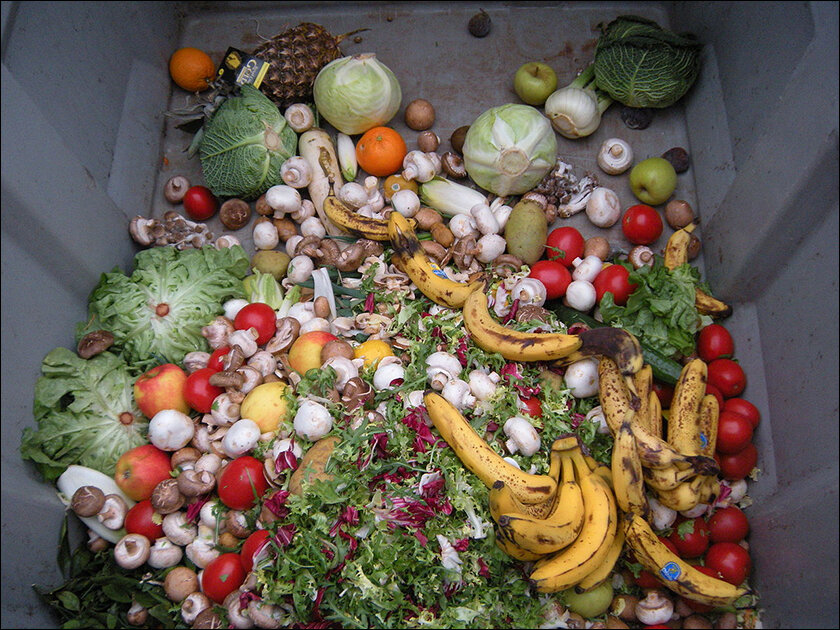

Attempts have been undertaken to reduce food waste. They include innovative technologies that have been employed by businesses and individuals to create food-saving actions that benefit both people and the environment.
In this post, we will talk about the different solutions provided by technology to solve the food waste problem.
1. Smart Inventory management systems
The best way to address food wastage is dealing with it where it’s being produced and distributed. Industries can utilise advanced inventory management systems based on cutting-edge technology. These systems include sensors, reference ID tags, and data analytics to help monitor stock levels in real time. This prevents food from being overstocked or allowed to expire before being consumed.
Shelf Engine is a Seattle-based application co-founded by Stefan Kalb in a bid to minimise food waste distribution areas specifically at grocery stores through the use of smart inventory systems. Shelf Engine was launched in 2016 and relies on machine learning and artificial intelligence to create grocery orders for some of the biggest grocery store chains in the United States.
Shelf Engine features five data streams that include sales figures, planned discounts and promotions, shipping information, and other factors such as weather forecasts, school calendars, and public holidays. The fifth data stream is data collected by various teams positioned across the country who go from store to store and track what is going on. The Shelf Engine team uses data analytics to forecast specific things using this data.
They can, for example, forecast how many of a given product will be sold on which days of the week and vice versa. With this information, grocery businesses can track their orders depending on what is needed, avoiding overstocking, which leads to food waste.
2. Use of food donation platforms
People all across the world have created dedicated smartphone apps to offer alternatives for re-allocating food surplus from supermarkets, restaurants, and homes, sparing food from going to waste with the press of a finger.
Too Good to Go is a Danish software that allows people in Europe and North America to buy extra food at reduced prices from stores and restaurants. Similarly, Yindii and Treatsure are mobile apps used in Thailand and Singapore that connect consumers with food and beverage shops that offer discounts on excess food at the end of each day. Users in over a hundred countries can use such apps to distribute extra food to those in need. These steps contribute significantly to reducing food waste.
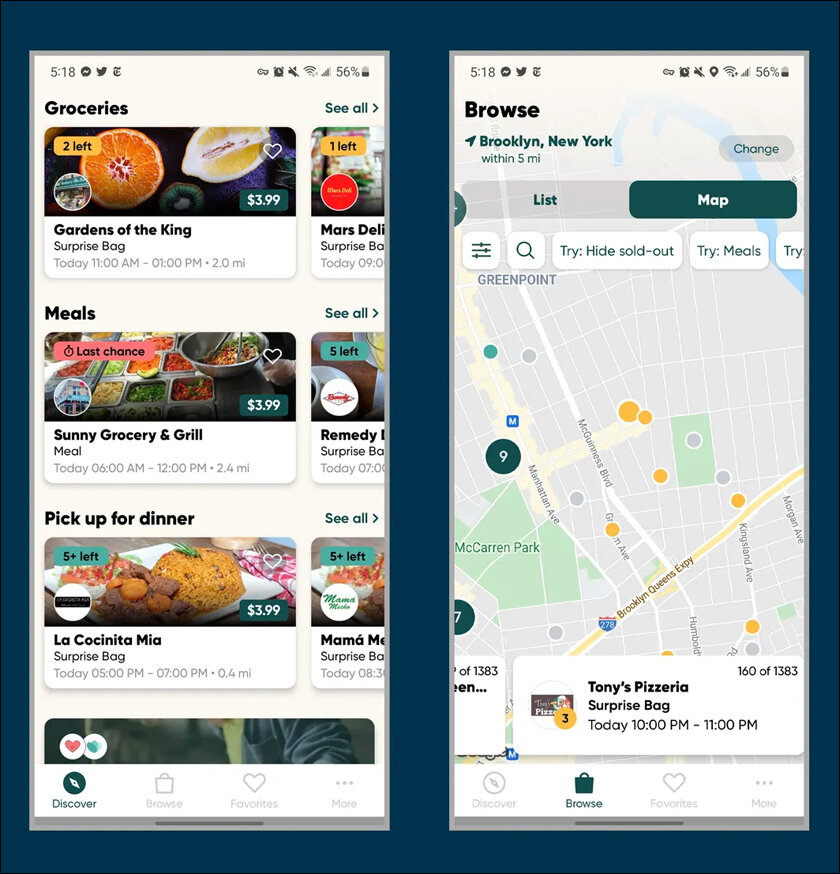
In southern India, apps like No Food Waste are used to facilitate the collection of extra food from businesses, enough to feed 100,000 people every month in Tarachi city alone. FoodCloud in Ireland is a social enterprise app that allows food businesses to upload information about their stock, alerting charities to collect and distribute any surplus.
3. Food tracking apps
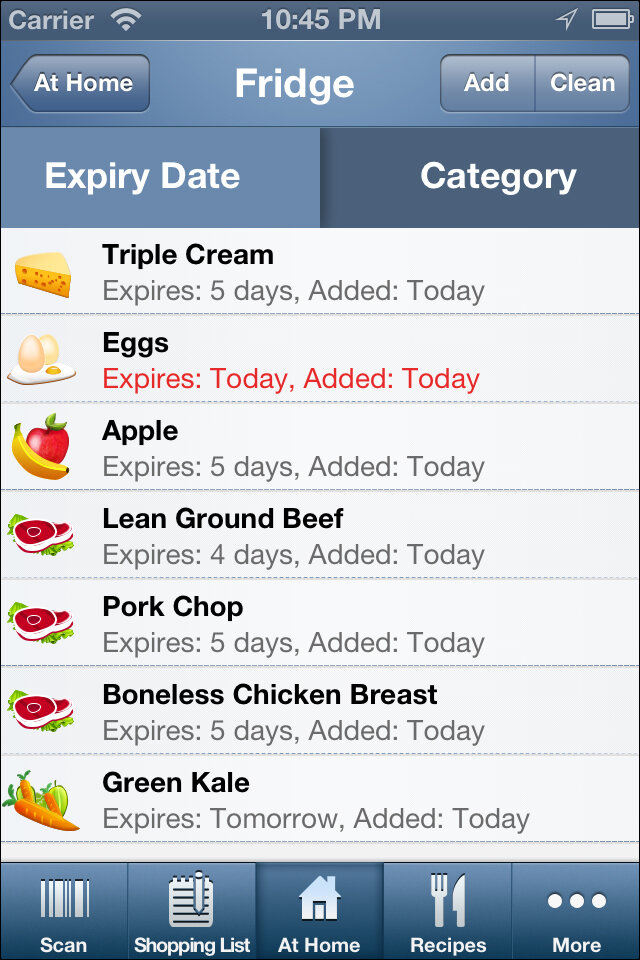
(Image Credit: Fridge Pal / Facebook)
Individuals can now track their own consumption from the comfort of their phones by using food tracking applications. Food tracking applications like Spoilage Tracker and Fridge Pal are fantastic examples. These apps allow users to enter the products in their refrigerators and pantry, as well as their expiration dates. For certain foods that do not contain expiration dates, the app allows the user to scan the barcodes to obtain expiration dates. The software can thus track the freshness of groceries.
Food tracking applications can also recommend customised meal plans based on the contents of the refrigerator. Fridge Pal, for example, might recommend dishes based on the contents of the fridge, preferring goods with shorter expiration dates and those are simple to prepare. Food tracking applications are being used to encourage timely consumption of food, hence preventing food from spoiling or being thrown away.
Technology has brought remedies to the severe food waste problem that has existed for many years. Technology has shown to provide rapid and effective ways of minimising food waste, from food tracking applications to the usage of data-driven inventory systems, and has done a better job of aligning food supply with food demand.
In case you missed:
- None Found







1 Comment
Great insights Felista! They will surely help with food wastage