AIoT has been around for a decade, but few know how transformative it can be to your business and life, writes Satyen K. Bordoloi.
The world is overflowing with information. From your heartbeat to the movement of clouds and stock markets, we have data about everything but intelligence about nothing. Adding to this flood is the Internet of Things (IoT); devices with sensors that create more data, overwhelming our minds.
What if we could address this problem by adding a layer that analyses all the data to make sense of it and provide useful insights that we can action? This idea is behind the marriage of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and IoT.

While IoT devices just gather information – like modern, high-end cars have tyre pressure detectors that display pressure on the dashboard screen – AioT devices add a layer of intelligence atop this data by e.g. pinging until you increase tyre pressure. This difference can be life-saving. For example, a smartwatch as an IoT device records your heart rate and BP. But with AI, it can detect abnormal patterns, like a heart attack, and alert you or a contact, potentially saving lives.
This fusion leverages IoT’s connectivity with AI’s data-driven insights, creating intelligent systems capable of real-time data collection, analysis, and action. Despite being around for over a decade, recent advancements in AI, especially GenAI, mean it is poised to revolutionise various industries. Hence, understanding AIoT is crucial.

What is AIoT?
AIoT stands for Artificial Intelligence of Things and denotes systems that integrate AI systems into IoT infrastructure. AI are smart systems that simulate human intelligence to enhance efficiency and enable new products and services. While, IoT is a network of connected devices that collect and transfer data in real time through embedded software or sensors, facilitating high levels of automation.
Combining AI and IoT means using AI to process data generated by IoT systems. Machine Learning (ML) and Deep Learning (DL) models in AI systems are integrated into IoT’s connectivity, thus enabling these systems to not only collect and transfer information but also understand and analyse it, potentially leading to life-changing results like a smartwatch detecting anomalous heartbeats and alerting the wearer.
This integration moves machine learning capabilities closer to the data source, known as Edge AI or Edge Intelligence, allowing for higher scalability, robustness, and efficiency.
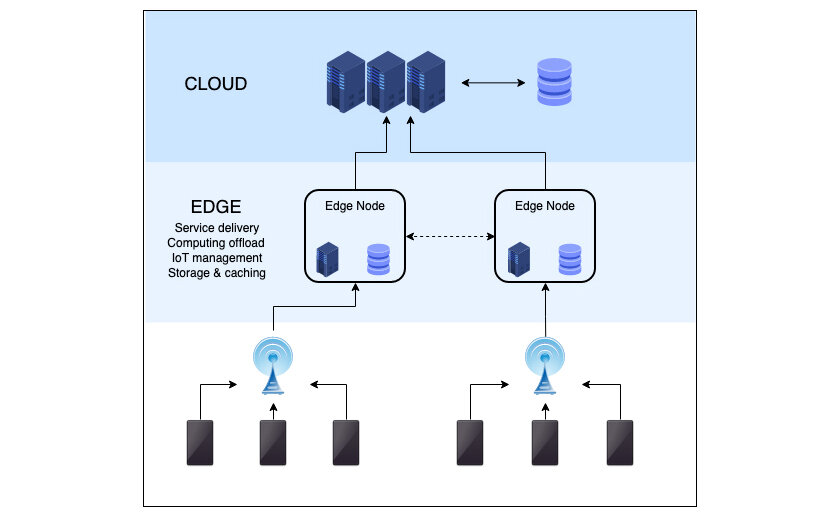
The Role of Edge Computing in AIoT
Edge Computing is growing in popularity because it acts like a crucial facilitator in emerging technologies such as IoT, 5G, and AI. It moves data processing from the cloud to the network edge, promoting distributed system designs with on-device data processing, which is efficient, scalable, robust, and suitable for low-latency use cases.
Initially, ML and DL were confined to the cloud due to high computational requirements. However, with advancements in computing enabling better edge intelligence, AIoT applications can now be efficiently supported at the network edge, achieving the fast-processing capacity and low latency required for intelligent IoT applications.

On-Device Machine Learning with AIoT Devices
Advances in hardware and machine learning have accelerated the deployment of billions of interconnected, intelligent, and adaptive devices in critical infrastructures such as healthcare, environmental control, logistics, transportation, and agriculture. Moving AI processing from the cloud to edge devices addresses bottlenecks, latency, and privacy issues associated with cloud-based AI applications. This edge-to-cloud AI architecture allows data to be generated and processed at the edge, with processed insights sent to the cloud as per user settings.
Compared to traditionally low-powered IoT devices, AIoT demands edge devices with sufficient computing power to perform on-device ML tasks. Current computational constraints limit the resource capacity and power utilisation of edge devices. Thus, AIoT applications must balance hardware cost and performance with optimised AI models and application design. Smaller, more efficient “lightweight” ML models can run on low-power devices like mobile phones, SoCs, or embedded computers. Examples include on-device ML model versions like TensorFlow Lite or Lightweight OpenPose.
Embedded machine learning on-device transforms AIoT devices into smart, intelligent systems capable of processing data independently. Technical advances in various fields have made it possible to apply AI technology efficiently, allowing for the development of real-world applications that were previously unattainable.

Benefits of Combining AI with IoT
AIoT enables AI adoption across industries to solve real business problems more effectively than traditional methods. Several benefits of combining AI with IoT include improved efficiency and reduced costs.
AIoT-powered machines can generate and analyse data, recognise patterns, and provide operational insights swiftly. This capability allows for the detection and resolution of problems, increasing the automation of manual processes and enabling companies to provide better services with a smaller workforce. For example, vision-based quality inspection and the use of cameras for quality control in industrial automation are efficient tools for adherence to guidelines and regulations.
Real-time monitoring of systems through AIoT can save time and reduce expensive business interruptions. Constant supervision by the system detects anomalies, makes predictions, and makes decisions without human intervention, achieving faster, objective results. An example is the use of industrial AI on IoT in the oil and gas sector, such as cameras for remote leakage detection.
Intelligent AIoT devices and systems are already playing a crucial role in reducing operational costs by enabling higher resource efficiency. For example, smart building applications adjust light and temperature controls based on occupancy. AIoT devices are also essential in preventive maintenance and machinery analysis in smart factories, where sensors and cameras monitor machine parts to avoid failures and expensive business interruptions.
Risk management is another critical area where AIoT excels. Distributed, intelligent systems can predict future risks and take preventive measures. Examples include water level analysis, employee safety analysis, and crowd analysis in public places. Even insurers have started using such applications to manage insurance risks for machines and entire factories.
AIoT Applications Across Industries
The adoption of AIoT is a rapidly growing technology trend across various industries, including logistics, agriculture, healthcare, manufacturing, surveillance, oil and gas, retail, and services. When loaded with specific sensors, computer vision for machines (machine vision) and predictive maintenance tools, they become Industrial IoT (IIoT).
We already use multiple AIoT devices without being aware of them. The Apple Watch is one example. Another is autonomous vehicles, which are loaded with sensors like lidar, radar, cameras, and other sensors, including on-device AI and ML algorithms that analyse information from multiple sources in real time to make accurate driving decisions.
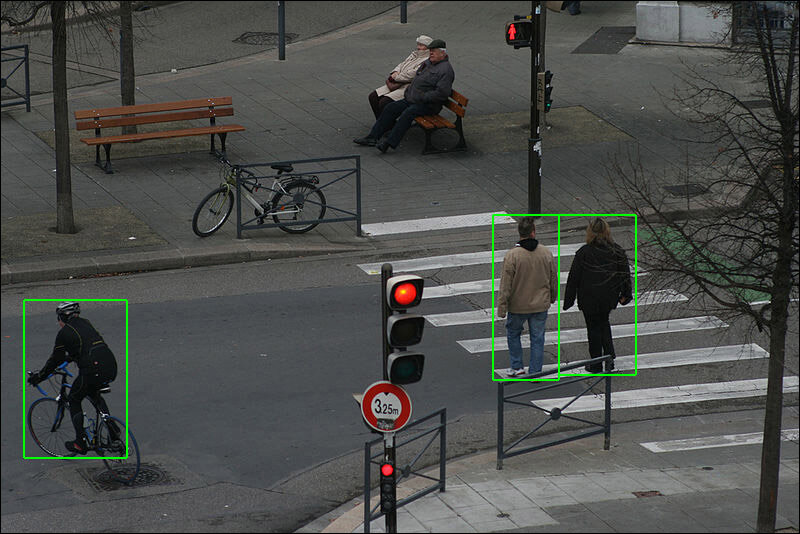
Video surveillance and security is another, controversial use case of AIoT. Traditional video surveillance requires a person to watch multiple video feeds. AIoT combines machine learning with video feeds to analyse data in real time, detect objects, recognise people, and identify events automatically. Walmart uses AIoT to detect theft, and police in many smart cities use it to analyse traffic violations. Authoritarian regimes, like China, use them for crime detection and to monitor dissidents. IIoT is used across industries to detect defects in machines. Many hotels use AIoT to detect room occupancy in real time.
These are just a few use cases. From retail to manufacturing, healthcare, security, oil and gas, banking, and insurance, industries using AIoT-powered solutions are increasing by the day. AI might have changed the world, but it is through AIoT that it will truly transform it beyond anything we can imagine today.
In case you missed:
- Collaboration, Complexity, & Innovation: Understanding Multi-Agent Systems
- The Path to AGI is Through AMIs Connected by APIs
- You’ll Never Guess What’s Inside NVIDIA’s Latest AI Breakthrough
- The Great Data Famine: How AI Ate the Internet (And What’s Next)
- Microsoft’s Quantum Chip Majorana 1: Marketing Hype or Leap Forward?
- Apple Intelligence – Steve Jobs’ Company Finally Bites the AI Apple
- Unbelievable: How China’s Outsmarting US Chip Ban to Dominate AI
- AI Taken for Granted: Has the World Reached the Point of AI Fatigue?
- AI Washing: Because Even Your Toothbrush Needs to Be “Smart” Now
- Copy Of A Copy: Content Generated By AI, Threat To AI Itself









