Spending on cybersecurity increased exponentially in the past 10 years and is showing no signs of slowing…
Spending in the cybersecurity industry was a whopping USD 80 billion in 2023 alone, with the number projected to cross USD 87 billion by the end of 2024. Despite this staggering investment, hackers are still exploiting vulnerabilities, and intercepting network, application, and device communications.
In fact, cybercrime is expected to inflict damages worth nearly USD 10.5 trillion by 2025, according to a Cybersecurity Ventures report. Nowadays, attacks are state-of-the-art, outwitting all traditional security methods including cryptography, key management, authentication, and even privacy challenges. Now many enterprises are rethinking the systems responsible for the creation of these vulnerabilities in the first place, and one technology that has emerged as a potential game-changer is blockchain.
A New Cybersecurity Approach
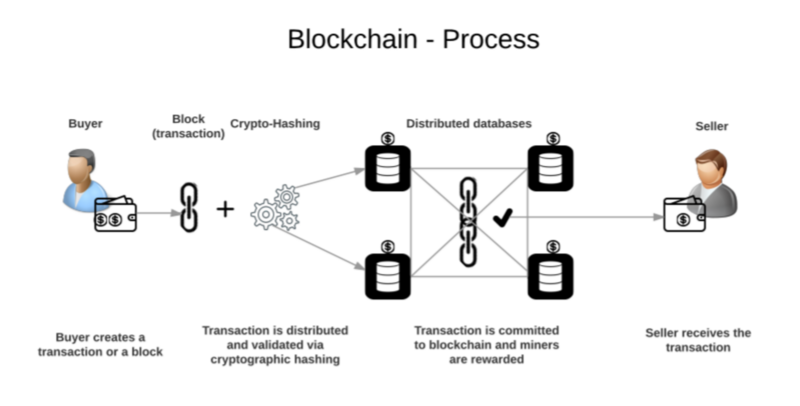
Blockchain is a path less travelled toward greater security and it is not as hospitable to cyber criminals. It not only verifies integrity and ownership effectively but also provides strong encryption and reduces vulnerabilities. Moreover, it can also eliminate the need for passwords in some cases, which are often called cybersecurity’s weakest link.
One of the chief advantages of blockchain is the fact that it employs a distributed ledger. This dispersed public key infrastructure model eliminates the most obvious targets, lessening many risks associated with centrally stored data. What’s more, since transactions are recorded in each node across the network, it is difficult for hackers to tamper with, compromise, or steal data, unless the platform itself is vulnerable.
Another traditional weakness that blockchain eliminates is the need for a central authority, thanks to its collaborative consensus algorithm that watches for false positives, anomalies, and malicious actions proactively. After all, you can fool one pair of eyes, but not all of them. This not only strengthens authentication but also secures record management and data communications.
Despite blockchain containing many non-traditional features, it does possess one of cybersecurity’s most important tools, which is encryption. The distributed ledger utilizes public key infrastructure for validating configuration changes, authenticating devices, securing communication, and discovering confidential devices in an Internet of Things (IoT) ecosystem.
Via digital signatures and encryption, blockchain can shield everything from connected security cameras, smart doorbells, and thermostats to other vulnerable edge devices. This is incredibly important, given that a 2020 Palo Alto Networks report described IoT device traffic as “low-hanging fruit for attackers”, as 98% of all traffic was unencrypted.
Using Blockchain to Enhance Cybersecurity
There are a lot of compelling features that blockchain offers that can enhance cybersecurity significantly.
Data Immutability and Integrity
Data immutability and integrity are prime when it comes to the cybersecurity realm, and blockchain excels in both. Once transactions are recorded on the blockchain, they become nearly impossible to alter. Hence, the data remains tamper-proof and secure. Unsurprisingly, this feature is applicable across many critical systems, such as supply chain management, legal documents, and even medical records. With blockchain protecting data, it becomes an impregnable fortress against any unsanctioned changes.
Secure Transactions
As we explained earlier, cryptographic security measures further fortify blockchain transactions, making it exceedingly challenging for cybercriminals to forge or tamper with transactions. This high level of security is critical for sensitive data exchanges, including financial transactions. The overall risk of unauthorized access and fraud access is dramatically reduced, if not eliminated, by leveraging blockchain.
Decentralization
Traditionally centralized systems are quite susceptible to single points of failure, making them lucrative targets for hackers. One of the biggest advantages of blockchain is that it operates on a decentralized network, thus reducing the risks associated with a single point of failure. It fortifies the overall network security, making it quite an impossible target for cyberattacks.
Improved Authentication
Blockchain technology augments user authentication processes by providing a decentralized and secure identity verification system. Users have complete control over their digital identities, thus reducing the risk of unauthorized access to personal information and identity theft. In a world where data breaches occur almost every day, blockchain’s robust authentication mechanisms are significantly important and advantageous.
Ensuring Redundancy
Since a distributed Blockchain is continually and simultaneously present in multiple locations, different computers end up maintaining copies of blockchain data. So, you can locate the original data in other sources in the event of deliberate or inadvertent manipulation.
In the end, blockchain represents a groundbreaking shift in reinforcing information security and securing data integrity. It makes for a transparent and immutable ledger that is bolstered against all traditional digital vulnerabilities, with the potential to solve the trust problem in the digital era. Educational efforts to broaden its acceptance and understanding are increasing, helping liberate it from being viewed primarily as a financial tool and showcase its true versatility and potential for adoption in many fields. Thus, blockchain could potentially be a new chapter in the safeguarding of our digital interactions and infrastructure.
In case you missed:
- All About Attack Surface Management
- How Blockchain Can Solve AI’s Trust Problem
- Enterprise Network Transformation: Benefits and Challenges
- Everything you need to know about Pi Network
- Tackling The Most Critical Cloud Security Vulnerabilities
- AI-Red Teaming: How Emulating Attacks Help Cybersecurity
- Cryptography in Network Security – Concepts and Practices
- AI Firewalls and How They Protect Your Data
- Password Practices For A Safe Digital Presence
- Top cloud migration myths